Moringa oleifera: A Sustainable Feed Additive for Poultry Nutrition
The modern poultry industry faces immense challenges—from antibiotic resistance and heat stress to the demand for safer, organic feed alternatives. Amidst this search for natural solutions, Moringa oleifera, popularly known as the drumstick tree or horseradish tree, has emerged as a botanical marvel. Native to India and now cultivated worldwide, Moringa oleifera is renowned for its exceptional nutritional, medicinal, and antimicrobial properties. Recent scientific reviews have highlighted its potential as a sustainable and powerful natural feed additive in poultry nutrition.
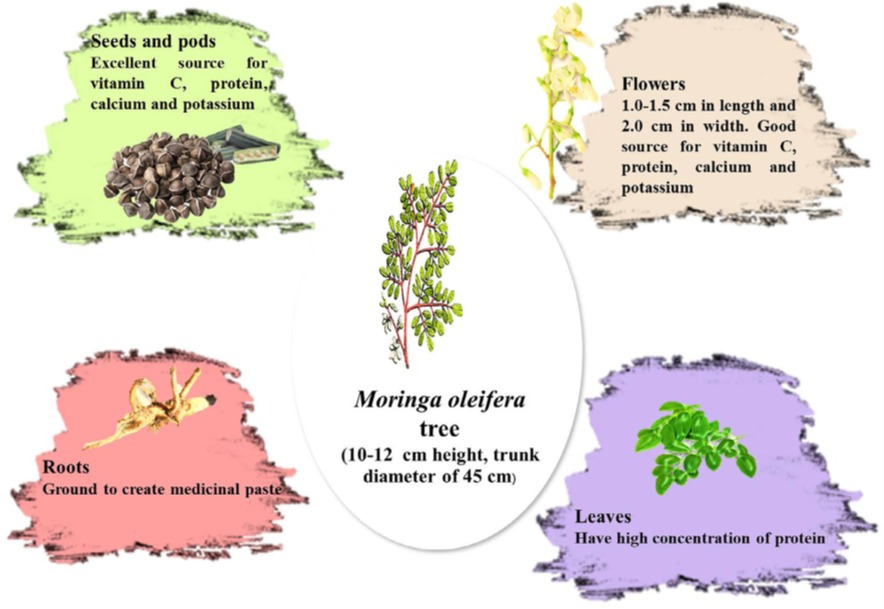
Figure 1: The nutritional contents of each part of Moringa oleifera tree
1. Nutritional Profile of Moringa oleifera
Moringa oleifera leaves are an abundant source of proteins, vitamins, and essential minerals, making them an ideal candidate for animal feed. Studies have shown that its leaves contain:
- Crude Protein: 25–30%
- Calcium: 3.65%
- Iron: 490 mg/kg
- Vitamin A, B, and C in high quantities
- Essential amino acids like methionine, lysine, and threonine
Beyond nutrition, moringa leaves also exhibit high digestibility and energy values, improving feed efficiency and productivity in poultry.
Learn how similar plant-based solutions support nutrition in our blog on Phytogenic Feed.
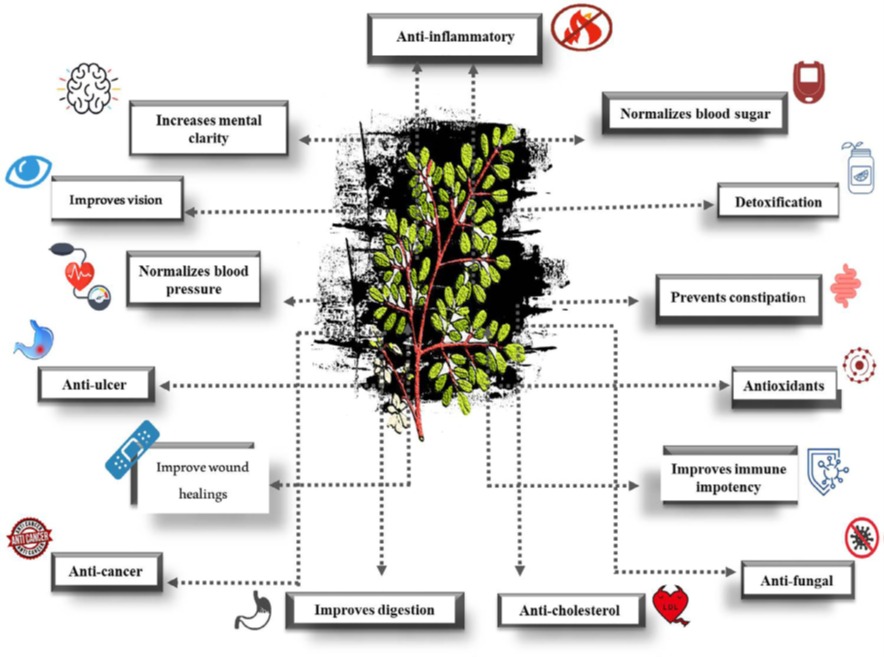
2. Phytochemicals and Antioxidants: Nature’s Defense
Moringa’s leaves are rich in phytochemicals such as flavonoids (quercetin, kaempferol), phenolic acids, and isothiocyanates. These compounds provide a wide range of pharmacological benefits, including:
- Antioxidant activity: Neutralizing harmful free radicals
- Anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects
- Cardioprotective and hepatoprotective properties
Compared to many vegetables and fruits, Moringa oleifera boasts a significantly higher antioxidant capacity—making it an excellent natural additive for enhancing animal health and immunity.
For stress management strategies, read Mitigating Heat Stress in Poultry Through Nutritional Strategies.
3. Antimicrobial and Bioenhancing Properties
One of the most striking aspects of Moringa oleifera is its broad-spectrum antimicrobial potential. Research indicates that extracts from its leaves, seeds, and roots exhibit activity against numerous pathogens, including:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- E. coli
- Salmonella typhi
- Candida albicans
Additionally, moringa seeds contain natural coagulants capable of water purification, an attribute useful in both agriculture and public health.
Furthermore, moringa’s bioenhancing compounds, such as niaziridin, can boost the absorption and effectiveness of antibiotics and nutrients—potentially reducing the need for synthetic drugs in poultry management.
Discover complementary antimicrobial solutions in Cinnamon in Poultry Feed: A Natural Alternative to Antibiotics.
4. Application in Poultry Diets
The inclusion of Moringa oleifera leaf meal in poultry diets has demonstrated multiple benefits:
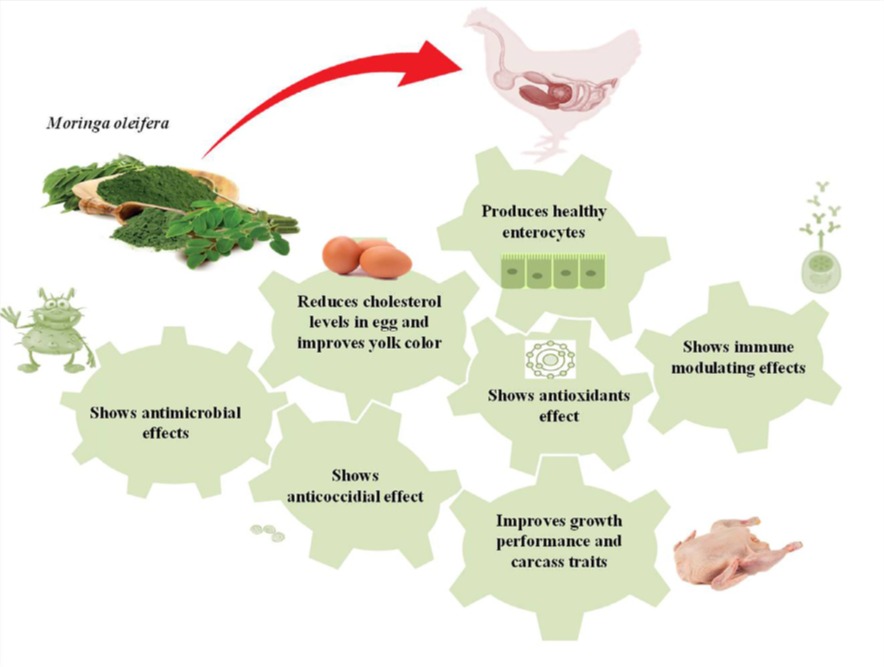
Figure 2: The impacts of applying Moringa oleifera leaves in poultry diets
- Improved growth performance and feed conversion ratio
- Enhanced egg quality, particularly yolk color and nutritional profile
- Reduced cholesterol levels in eggs
- Strengthened immune response and gut health
However, moderation is key. Studies recommend the following safe inclusion levels:
- Broiler diets: 5–10% leaf meal
- Layer diets: up to 10%
- Higher inclusion (>15%) may reduce feed palatability and digestibility due to antinutritional factors like tannins and phytates.
Enhance gut health further with enzymes see Enzymes in Poultry Nutrition: Enhancing Efficiency and Sustainability.
Figure 3: Medicinal properties of Moringa oleifera tree
5. Beyond Poultry: Environmental and Industrial Applications
Moringa oleifera is not just beneficial for animals—it offers eco-friendly applications across industries. Its seed oil, rich in oleic acid and tocopherols, is used in cosmetics and biodiesel production. The plant’s flocculant proteins are valuable for wastewater treatment, while its extracts act as natural fertilizers and growth promoters for crops.
6. Safety and Toxicity
Toxicological studies confirm safety at <1,000 mg/kg. Avoid excess bark/seed extracts due to glycosides. Proper processing ensures efficiency.
Conclusion
Moringa oleifera bridges productivity and sustainability in antibiotic-free poultry farming. At 5–10% inclusion, it boosts growth, immunity, egg quality, and feed efficiency—making it ideal for organic systems. As agriculture embraces green solutions, moringa nourishes flocks, protects health, and promotes environmental stewardship.
References
- Abd El-Hack, M.E., et al. (2022). Poultry Science, 101:102031.
- Fahey, J.W. (2005). Trees for Life Journal.
- Foidl, N., et al. (2001). Agricultural and industrial uses.
- Moyo, B., et al. (2011). African Journal of Biotechnology.
- Olugbemi, T.S., et al. (2010). Egg quality and cholesterol.